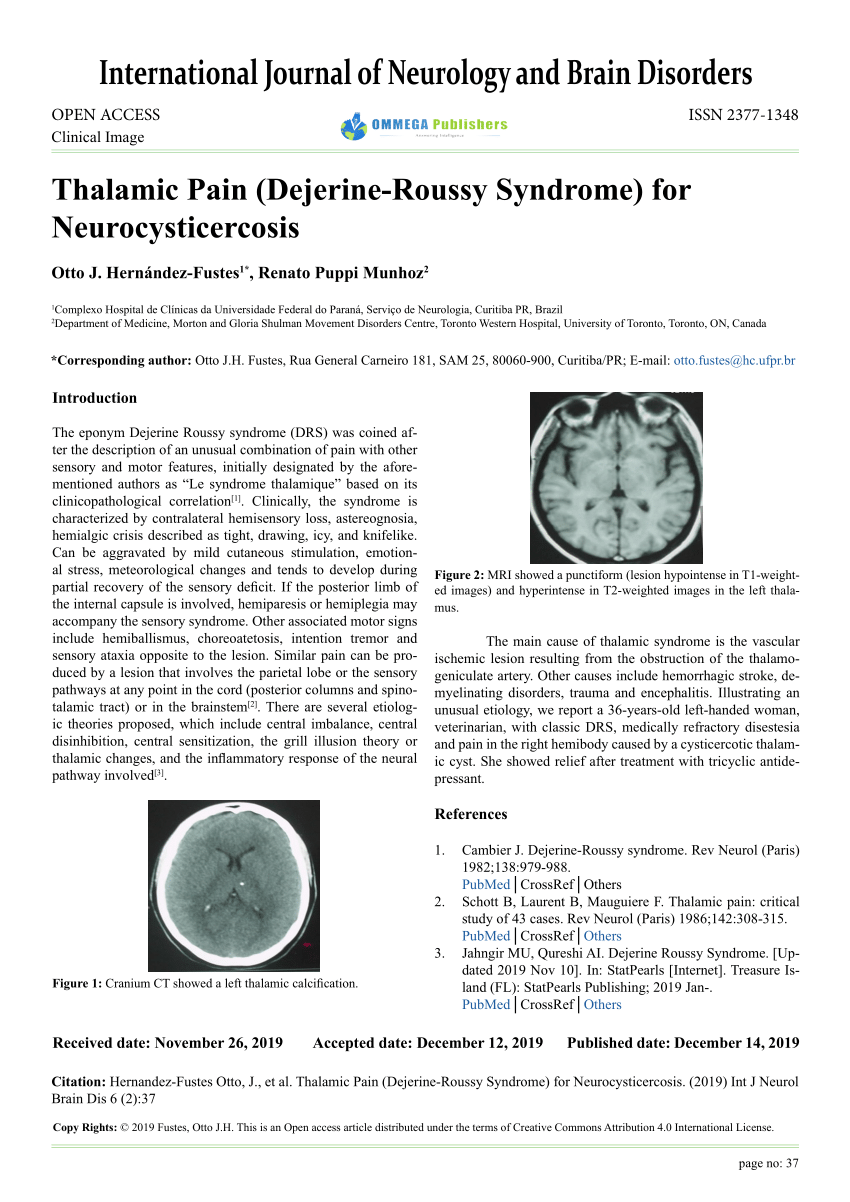
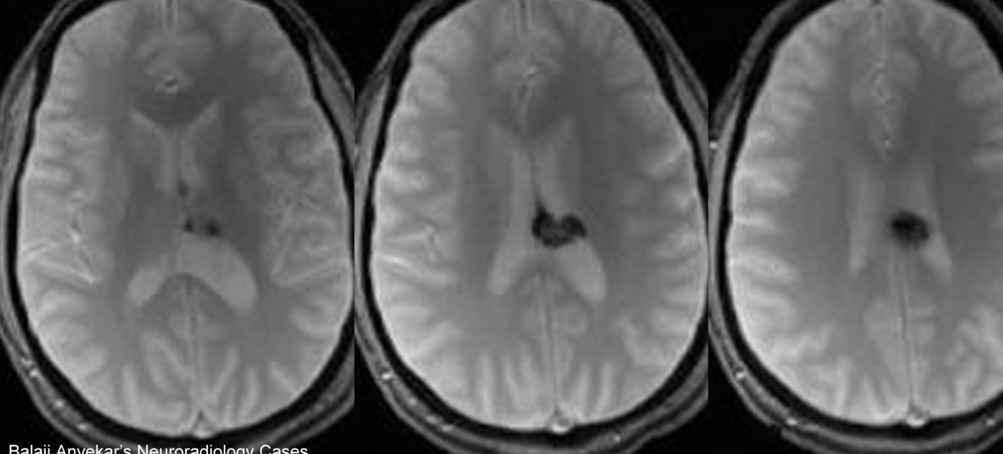
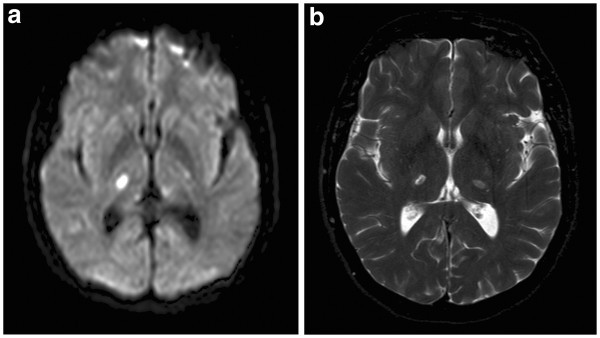
Dejerine-roussy Syndrome
Dejerine-roussy syndrome. Thalamic pain syndrome is now more commonly known as central post-stroke pain while historically it was known as DejerineRoussy syndrome. Los accidentes cerebrovasculares isquémicos y. The nuances in these various terms are as follows.
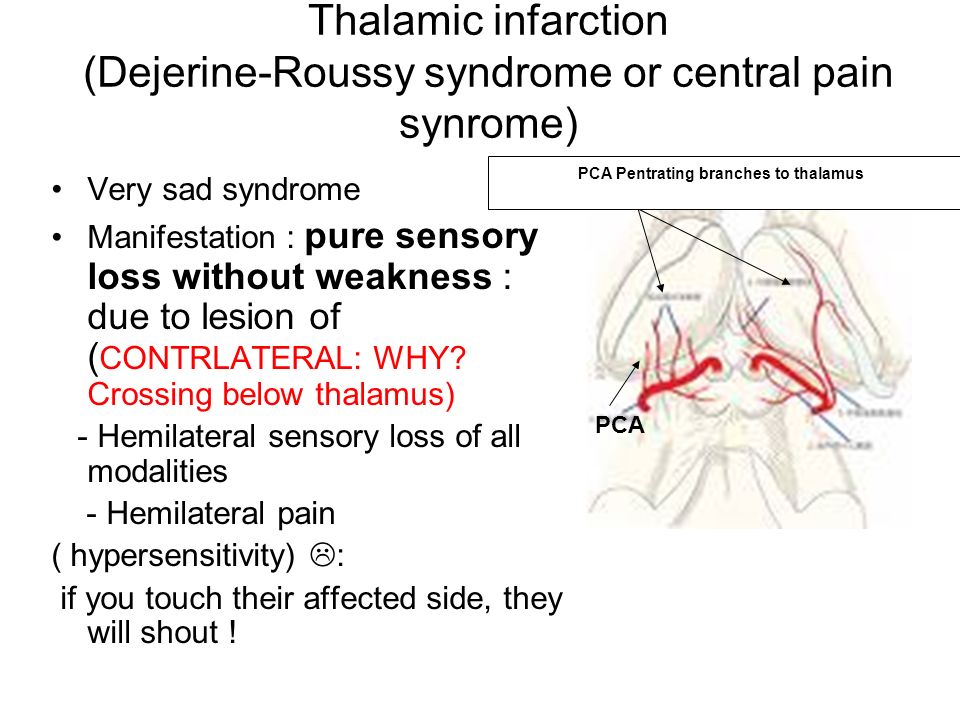
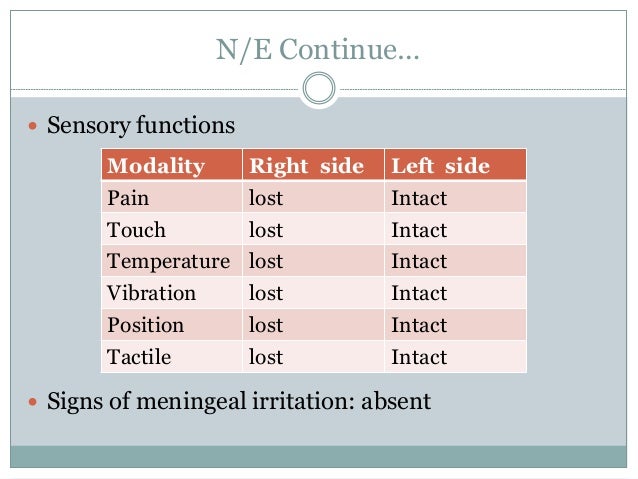
Patients develop dysesthesia or allodynia weeks to months after the initial stroke. Central post-stroke pain is a rare central neuropathic pain also known as Dejerine Roussy syndrome and thalamic pain syndrome occurs after infarction of the ventroposterolateral thalamus. Sented Thalamic Syndrome Dejerine-Roussy contralateral to the injury characterized by.
Dejerine Roussy syndrome is a rare central post-stroke pain which occurs due to involvement of the spinothalamic tract anywhere along its course from the lateral medulla to the inferolateral. Dejerine-roussy syndrome or thalamic pain syndrome is also referred to as Central Pain Syndrome CPS. CPSP previously known as Dejerine-Roussy syndrome and thalamic pain syndrome is a feared complication of cerebrovascular accidents and has been described by Tasker as among the most spectacular distressing and intractable of pain syndromes2 It affects approximately 8 of patients after a stroke but is more common after strokes that involve the lateral medulla and inferior-lateral.
La enfermedad de síndrome dejerine-roussy o síndrome de dolor talámico es pobre cuando se trata de una entrada sensorial normal. On June 7 1906 Jules Dejerine 18491917 and Gustave Roussy 18741948 presented to the Société de Neurologie de Paris the first description of the thalamic syndrome with serial-section microscopic images. Disturbances of deep sensiti-vity.
Una brisa e incluso un abrazo o un toque ligero e incluso ropa que toque la piel produce un dolor intenso y ardiente. El síndrome de Dejerine-Roussy o síndrome de dolor talámico es una afección que se desarrolla después de un accidente cerebrovascular talámico un accidente cerebrovascular que causa daño al tálamo. Joseph Jules Dejerine and Gustave Roussy first described it in.
Joseph Jules Dejerine and Gustave Roussy first described it in. 4 Four subtypes of Dejerine-Roussy syndrome have been identified through somatosensory evoked potentials each with set patterns of sensory loss. Central post-stroke pain is a rare central neuropathic pain also known as Dejerine Roussy syndrome and thalamic pain syndrome occurs after infarction of the ventroposterolateral thalamus.
They also provided the first account of central poststroke pain CPSP. Dejerine-Roussy syndrome has a number of synonyms Dejerine and Roussy formally described Thalamic syndrome in 1906 after Dejerine had used staining methods to show the route of the medial lemniscus to the thalamus.
Los accidentes cerebrovasculares isquémicos y.
Central post-stroke pain is a rare central neuropathic pain also known as Dejerine Roussy syndrome and thalamic pain syndrome occurs after infarction of the ventroposterolateral thalamus. They suggested that pain is one of the primary symptoms of. CPSP previously known as Dejerine-Roussy syndrome and thalamic pain syndrome is a feared complication of cerebrovascular accidents and has been described by Tasker as among the most spectacular distressing and intractable of pain syndromes2 It affects approximately 8 of patients after a stroke but is more common after strokes that involve the lateral medulla and inferior-lateral. Sonido luz vibraciones movimiento emociones de estrés e incluso pensar. Central post-stroke pain is a rare central neuropathic pain also known as Dejerine Roussy syndrome and thalamic pain syndrome occurs after infarction of the ventroposterolateral thalamus. Disturbances of deep sensiti-vity. Joseph Jules Dejerine and Gustave Roussy first described it in. On June 7 1906 Jules Dejerine 18491917 and Gustave Roussy 18741948 presented to the Société de Neurologie de Paris the first description of the thalamic syndrome with serial-section microscopic images. Dejerine-Roussy syndrome has a number of synonyms Dejerine and Roussy formally described Thalamic syndrome in 1906 after Dejerine had used staining methods to show the route of the medial lemniscus to the thalamus.
El síndrome de Déjerine-Roussy o síndrome talámico se caracteriza por hemiparesia leve transitoria hemicoreoatetosis hemihipoestesia hiperalgesia alodinia y hemiataxia con astereognosia de intensidad variable y se presenta ante lesiones de los núcleos posteriores del tálamo. Dejerine-Roussy syndrome has a number of synonyms Dejerine and Roussy formally described Thalamic syndrome in 1906 after Dejerine had used staining methods to show the route of the medial lemniscus to the thalamus. Dejerine Roussy syndrome is a rare central post-stroke pain which occurs due to involvement of the spinothalamic tract anywhere along its course from the lateral medulla to the inferolateral. La enfermedad de síndrome dejerine-roussy o síndrome de dolor talámico es pobre cuando se trata de una entrada sensorial normal. Dejerine-Roussy syndrome is a rare condition usually caused by ischemic or hemorrhagic strokes involving the thalamus. Los accidentes cerebrovasculares isquémicos y. The nuances in these various terms are as follows.





:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/stroke-56a80d425f9b58b7d0f03527.jpg)







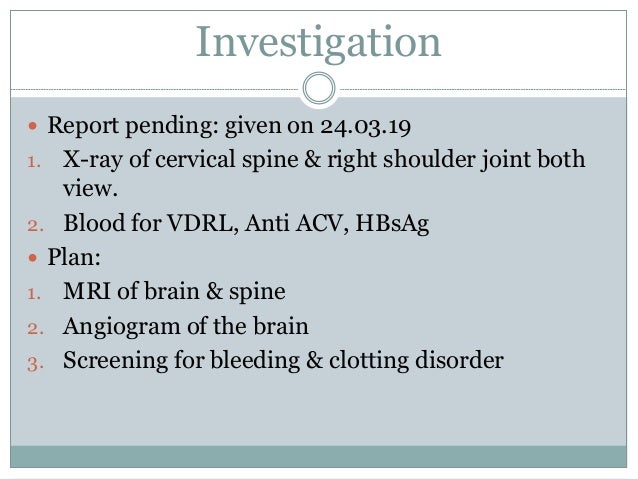




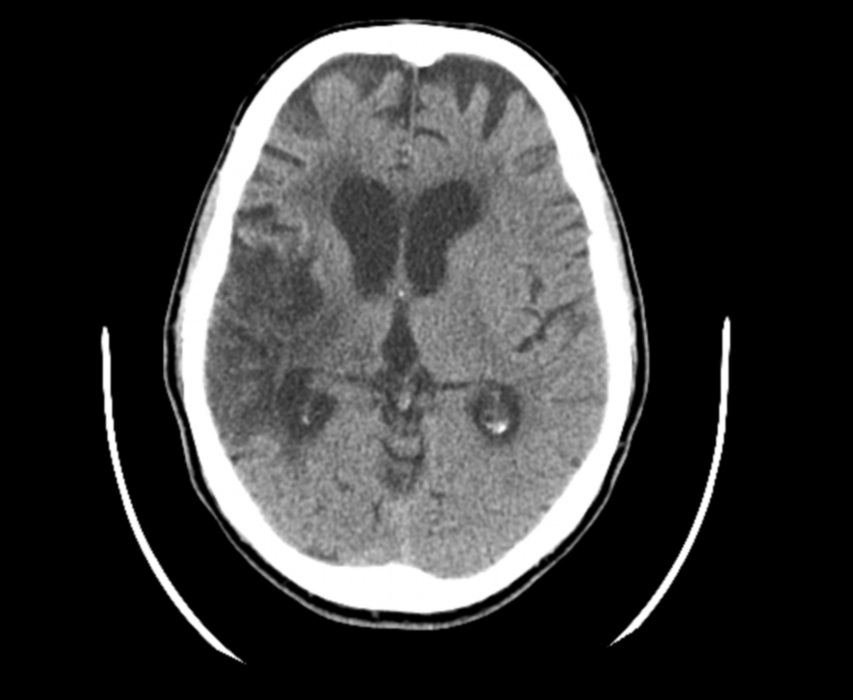
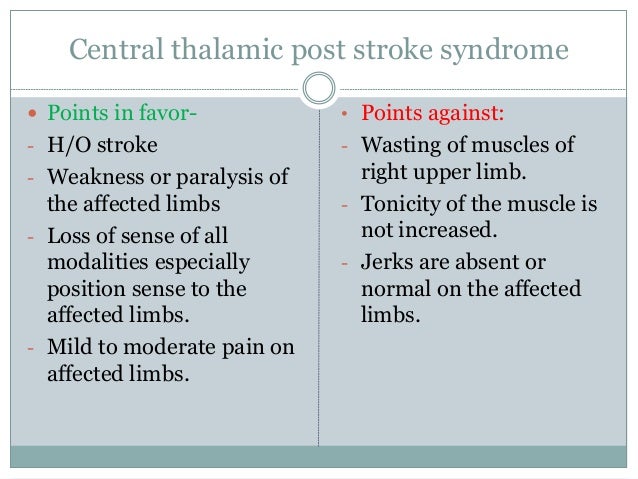
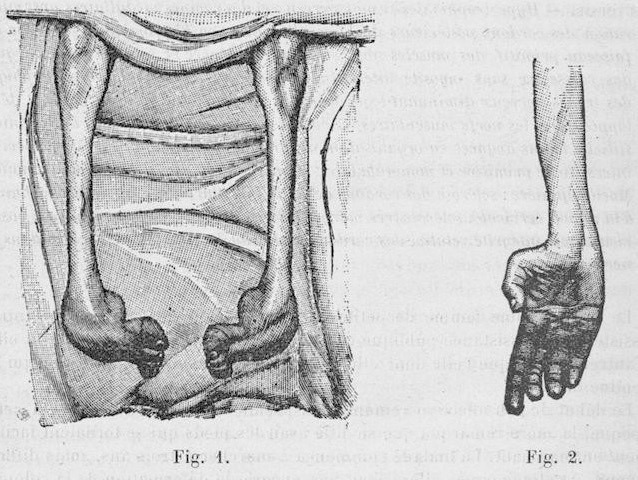


















Post a Comment for "Dejerine-roussy Syndrome"